Different types of popular expression system
1. Escherichia coli
t is the most widely used expression system, since it is the easiest, quickest and cheapest method. For project initialization and preliminary test, it is recommended to go with E.coli expression. Plenty of available commercial and non-commercial expression vectors with different N- and C-terminal tags, as well as different compatibilities. Hence, a rich selections of strains are optimized for various applications.
2. Bacillus subtilis
Bacillus subtilis is a gram-positive bacterial expression system - it is also easy, fast and cheap to operate. Unlike E.coli, B.subtilis contains only a single layer membrane and it also has a large excretory capacity, making it an optimal framework for secreted protein. After optimization B.subtilis is able to secret foreign proteins such as interferon, growth hormone, pepsinogen and epidermal growth factor with good quality and quantity. However, the degradability of foreign protein shall be concerned; the lacking of well-regulated inducible vectors is also limiting the application of the B. subtilis system.
3. Yeast
Yeast is an eukaryotic organism and has some advantages and disadvantages over E. coli. One of the major advantages is that yeast culture can be grown to very high density (up to 50g/L), which makes them especially useful for the production of isotope labeled protein for NMR. Post translation modification and secreted expression possibility making it more valuable in industry production. Two most used yeast strains are Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris.
4. Baculovirus infected insect cells
Compare to yeast, insect cell is a higher eukaryotic system which is capable to process more complex post-translational modifications. It consists the best mechanism for the protein folding which offer the best chance of obtaining soluble protein when you want to express a protein of mammalian origin. The disadvantages of insect cells are the higher costs and the longer duration before you get protein.
5. Mammalian cells
HEK (human embryonal kidney) or CHO (Chinese hamster ovary) cell lines are mostly used in labs as well as industries, in order to obtain more complex proteins which require proper post-translational modifications. Both cell lines can be used for both transient and stable cell line expression. Stable cell line is more time consuming due to the generation process, but it offers higher yield and less variation if long-term production is required. These expression systems have usually a high capacity of producing secreted protein (up to 1g per Liter, or several grams per Liter in stable cell line), while the ability of expressing intracellular proteins is usually much lower.
t is the most widely used expression system, since it is the easiest, quickest and cheapest method. For project initialization and preliminary test, it is recommended to go with E.coli expression. Plenty of available commercial and non-commercial expression vectors with different N- and C-terminal tags, as well as different compatibilities. Hence, a rich selections of strains are optimized for various applications.
2. Bacillus subtilis
Bacillus subtilis is a gram-positive bacterial expression system - it is also easy, fast and cheap to operate. Unlike E.coli, B.subtilis contains only a single layer membrane and it also has a large excretory capacity, making it an optimal framework for secreted protein. After optimization B.subtilis is able to secret foreign proteins such as interferon, growth hormone, pepsinogen and epidermal growth factor with good quality and quantity. However, the degradability of foreign protein shall be concerned; the lacking of well-regulated inducible vectors is also limiting the application of the B. subtilis system.
3. Yeast
Yeast is an eukaryotic organism and has some advantages and disadvantages over E. coli. One of the major advantages is that yeast culture can be grown to very high density (up to 50g/L), which makes them especially useful for the production of isotope labeled protein for NMR. Post translation modification and secreted expression possibility making it more valuable in industry production. Two most used yeast strains are Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris.
4. Baculovirus infected insect cells
Compare to yeast, insect cell is a higher eukaryotic system which is capable to process more complex post-translational modifications. It consists the best mechanism for the protein folding which offer the best chance of obtaining soluble protein when you want to express a protein of mammalian origin. The disadvantages of insect cells are the higher costs and the longer duration before you get protein.
5. Mammalian cells
HEK (human embryonal kidney) or CHO (Chinese hamster ovary) cell lines are mostly used in labs as well as industries, in order to obtain more complex proteins which require proper post-translational modifications. Both cell lines can be used for both transient and stable cell line expression. Stable cell line is more time consuming due to the generation process, but it offers higher yield and less variation if long-term production is required. These expression systems have usually a high capacity of producing secreted protein (up to 1g per Liter, or several grams per Liter in stable cell line), while the ability of expressing intracellular proteins is usually much lower.
Common applications, Pros and Cons of each expression system
Which expression system matches my protein/project - questions to be answered
1. What type of protein do I want to express?
If the protein is prokaryotic origin, obviously E. coli is the first choice. It is quick and cheap and the organism has all the mechanism for folding and post-translational modifications. B.subtilis is also optional, when soluble expression is required.
However, it has to be very careful when the full protein or a domain of the protein, show function of regulating bacteria growth/duplication, gene expression and/or essential life maintenance, the expression will have higher chance of fail. Is it means that as long as the protein show function of life maintenance, we can’t use bacteria expression system? The answer is “no”, because the tolerance of the bacteria is unsure before running any test! Hence, to try different strains, different induction strategy will .
When the protein is from an eukaryotic source, the method of choice will depend on more factors. For any type of preliminary study or simply to generate testing material it is still advised to use E.coli system.
2. Do I get soluble protein when I express in E. coli?
Eukaryotic protein expression use E.coli expression system is a common choice by reasons mentioned above. However, a significant percentage of eukaryotic proteins don't fold properly in E. coli and form insoluble inclusion bodies. By optimizing the culture condition, it is sometimes possible to improve the percentage of soluble protein. Hence the operation of resolubilize the protein from inclusion body is commonly used. Also your target protein can be expressed as fusion protein, by partnering with a solubility enhancing tag such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST), maltose binding protein (MBP), or DsbA. Often, however, instead of trying out 10 different E. coli constructs, it is better to switch to an eukaryotic expression system since the protein folding will be better done by an eukaryotic source.
3. Does my protein need post-translational modifications for structure/activity?
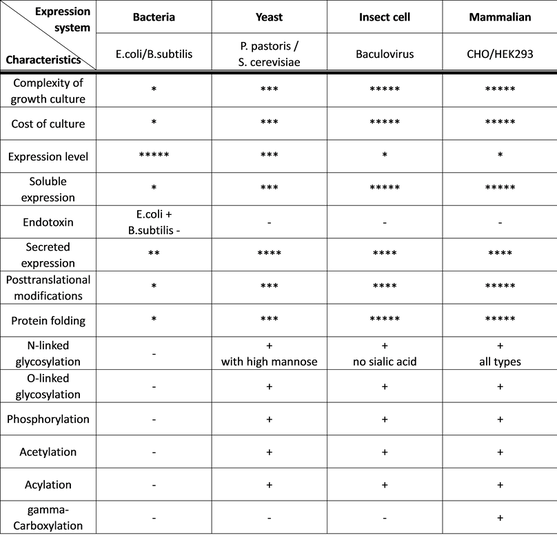
A certain percentage of the proteins require modifications following translation in order to become active and/or adapt the proper structure. To remove the N-terminal methionine residue is the elementary of these modifications, which can occur in all of the organisms. More complex modifications, like N- and O-glycosylation, phosphorylation, are exclusively carried out by eukaryotic cells. Note: not all eukaryotic cells carry out the same modifications! Check table under to find out which expression system carries out the post-translational modification(s) you are looking for.
4. What is the codon usage in my protein?
Thanks to the development of bioinformatics, we only need to use some software to optimize the codon before gene synthesis. In practical, different tools show slight different codon bias. If the aim of protein expression is to establish high expression cell line, it is better to test at least 2 variants of optimized sequences from tools of different sources.
If the protein is prokaryotic origin, obviously E. coli is the first choice. It is quick and cheap and the organism has all the mechanism for folding and post-translational modifications. B.subtilis is also optional, when soluble expression is required.
However, it has to be very careful when the full protein or a domain of the protein, show function of regulating bacteria growth/duplication, gene expression and/or essential life maintenance, the expression will have higher chance of fail. Is it means that as long as the protein show function of life maintenance, we can’t use bacteria expression system? The answer is “no”, because the tolerance of the bacteria is unsure before running any test! Hence, to try different strains, different induction strategy will .
When the protein is from an eukaryotic source, the method of choice will depend on more factors. For any type of preliminary study or simply to generate testing material it is still advised to use E.coli system.
2. Do I get soluble protein when I express in E. coli?
Eukaryotic protein expression use E.coli expression system is a common choice by reasons mentioned above. However, a significant percentage of eukaryotic proteins don't fold properly in E. coli and form insoluble inclusion bodies. By optimizing the culture condition, it is sometimes possible to improve the percentage of soluble protein. Hence the operation of resolubilize the protein from inclusion body is commonly used. Also your target protein can be expressed as fusion protein, by partnering with a solubility enhancing tag such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST), maltose binding protein (MBP), or DsbA. Often, however, instead of trying out 10 different E. coli constructs, it is better to switch to an eukaryotic expression system since the protein folding will be better done by an eukaryotic source.
3. Does my protein need post-translational modifications for structure/activity?
A certain percentage of the proteins require modifications following translation in order to become active and/or adapt the proper structure. To remove the N-terminal methionine residue is the elementary of these modifications, which can occur in all of the organisms. More complex modifications, like N- and O-glycosylation, phosphorylation, are exclusively carried out by eukaryotic cells. Note: not all eukaryotic cells carry out the same modifications! Check table under to find out which expression system carries out the post-translational modification(s) you are looking for.
4. What is the codon usage in my protein?
Thanks to the development of bioinformatics, we only need to use some software to optimize the codon before gene synthesis. In practical, different tools show slight different codon bias. If the aim of protein expression is to establish high expression cell line, it is better to test at least 2 variants of optimized sequences from tools of different sources.
- How to choose expression strategy for my specific protein?
- How to produce large quantity of protein?
- How to get my protein with 99% purity?